How QR Code Inspections Prevent Fraud
Original: https://cli.im/article/detail/2202
Compared to traditional paper-based inspection sheets that rely on manual recording, QR code inspections allow for the upload of on-site photos, videos, real-time location data, and other content that cannot be captured with paper. This content helps verify the authenticity of the inspection, thereby preventing fraud.
Building on this, CaoLiao provides several anti-fraud features that can be used in combination based on actual needs.
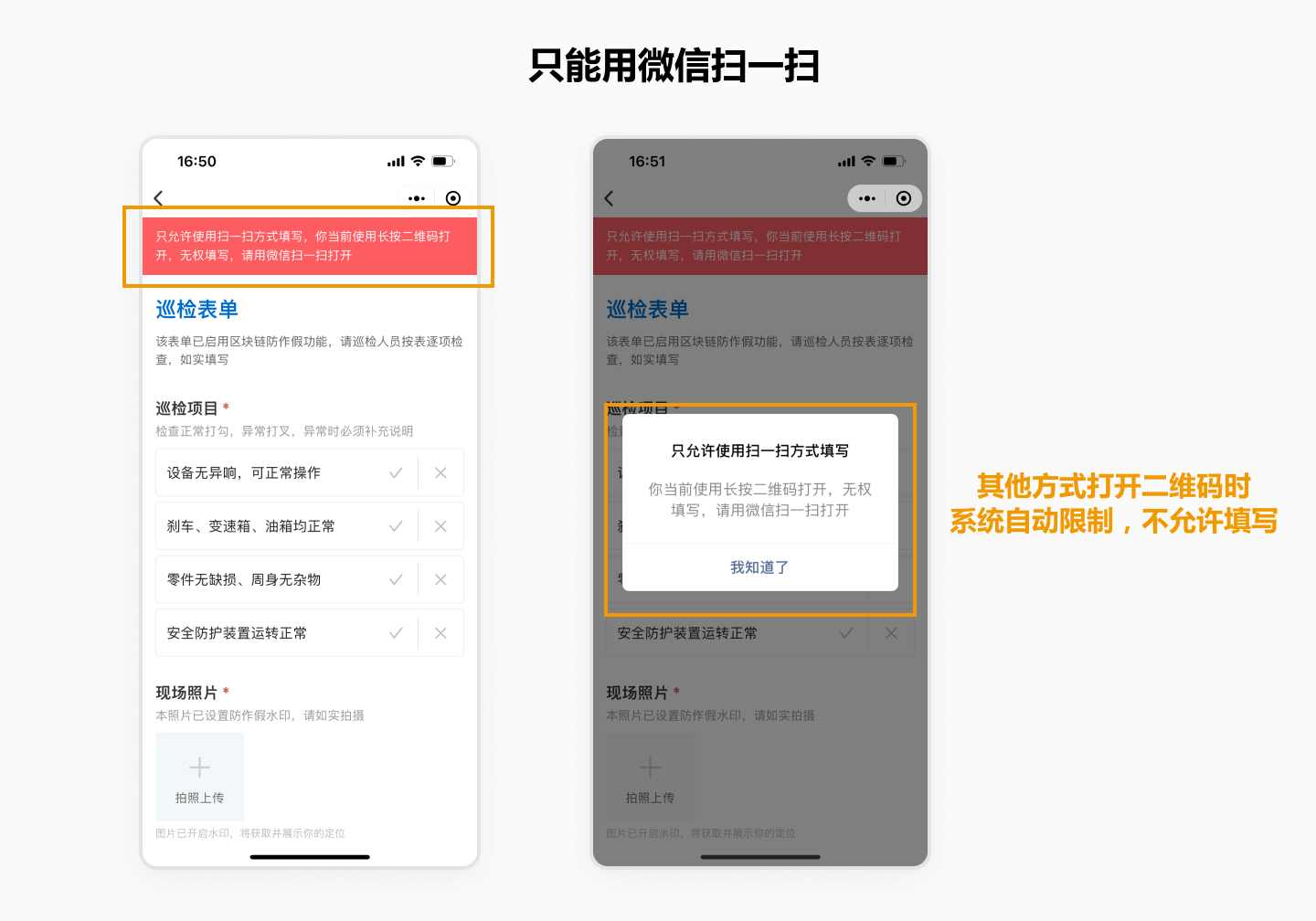
1. Restrict Scanning to WeChat Only
Inspectors can only scan the QR code using WeChat’s built-in scanner. They cannot open the QR code from images saved in their phone’s gallery. This prevents inspectors from saving the QR code image in advance and performing the inspection elsewhere.
Note: This feature cannot prevent inspectors from printing the QR code and scanning it with WeChat, or scanning a QR code image from someone else’s phone.
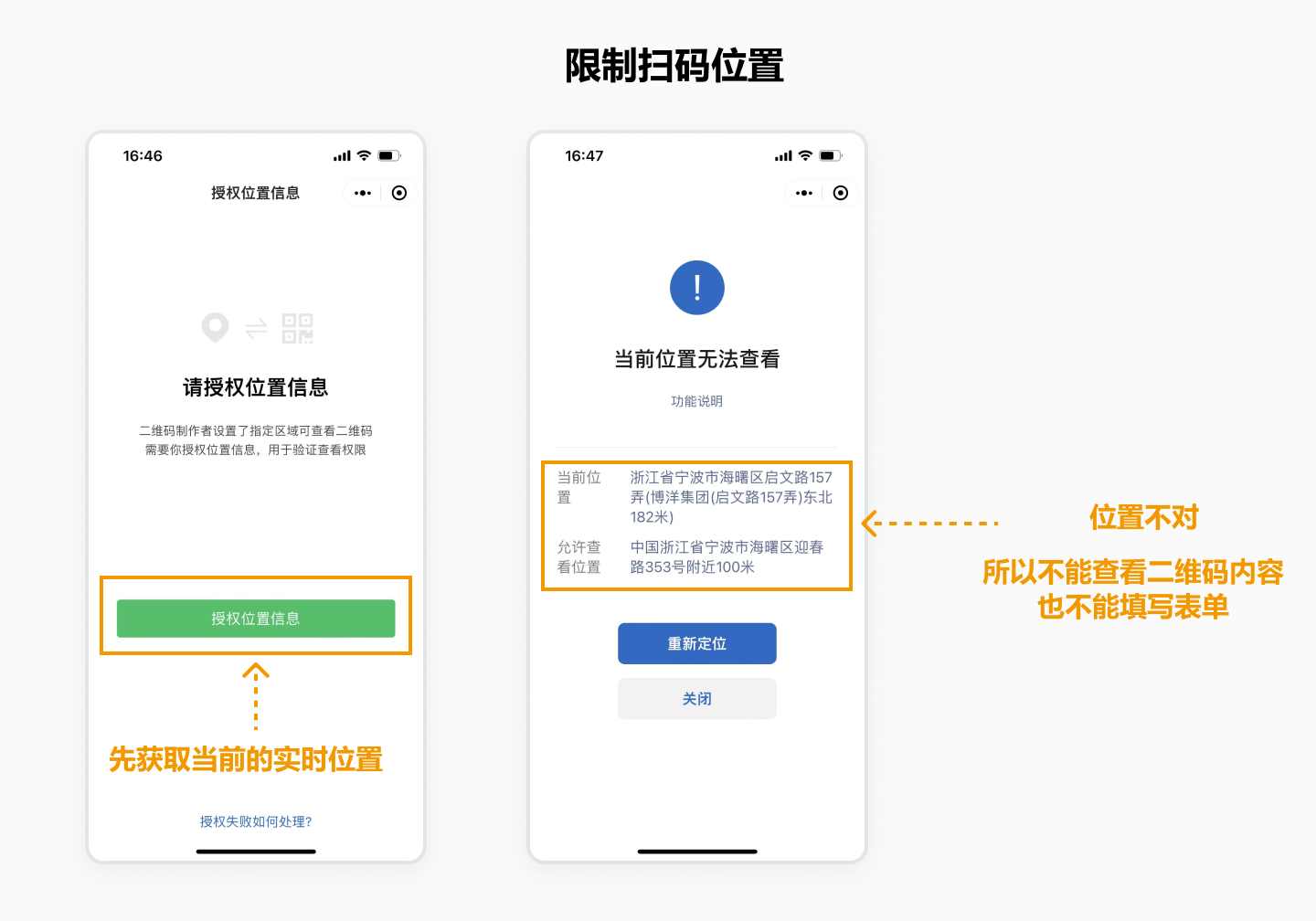
2. On-site Scanning Only (Location Restrictions)
The system captures the inspector’s real-time location when scanning the QR code. If they are not within the designated area, they cannot complete the inspection. This acts like an electronic fence, ensuring only those inside the fence can perform the inspection.
Note: The minimum range for this feature is approximately 100 meters around a specified location. Therefore, it is not suitable for highly precise location restrictions (e.g., a specific building in a factory) but is ideal for broader area restrictions.
3. On-site Photo Capture Only
The image component in the inspection form can be restricted to allow only photos taken on the spot to be uploaded. This prevents inspectors from selecting and uploading historical images from their phone’s gallery. However, this feature cannot prevent the reshooting of existing images.
4. Image Watermarking
Similar to a watermark camera, the system automatically adds a watermark to every photo uploaded during the inspection. The watermark includes details such as the photo timestamp, location, and the inspector’s information.

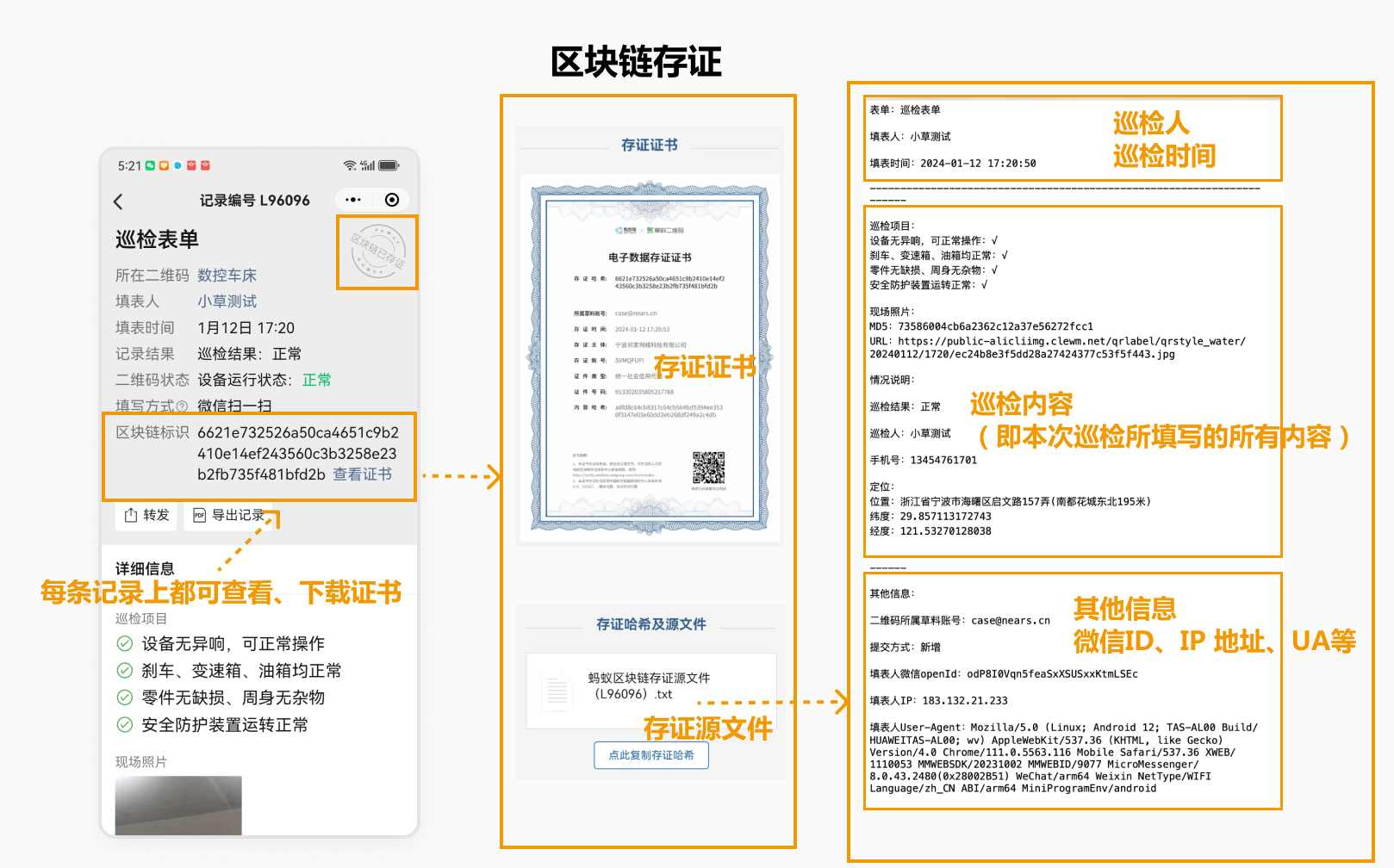
5. Blockchain Notarization for Fraud Prevention
This feature enables the notarization of each form submission on the Ant Blockchain. The notarization acts like an indelible and unalterable "watermark" for every inspection record.
Compared to image watermarks, blockchain notarization provides more comprehensive data. In addition to the text and images in the inspection record, it includes log data such as the mobile device model, IP address, and WeChat ID used during submission. Due to the immutability of blockchain, this serves as legally recognized electronic evidence. The combination of comprehensive data and tamper-proof characteristics ensures that each inspection record holds the same legal validity as a paper archive.
Of course, most daily inspection records do not require legal evidence. In routine management, this feature functions like a "surveillance camera" installed for each inspector, recording and preserving every inspection action for future traceability. When inspectors are aware that such a "camera" is monitoring their actions, the likelihood of fraudulent behavior is significantly reduced.
6. Summary
Overall, these anti-fraud features focus more on "monitoring" than on "restriction."
Managers can combine these monitoring methods to prevent fraudulent inspections. This approach keeps management costs manageable, maintains simplicity for inspectors, and facilitates the adoption of QR codes as a replacement for paper-based inspections.
If you have further questions about preventing fraud in inspections, feel free to ask or leave a comment anytime!