Effective Enterprise Work Safety Training
Original: https://cli.im/article/detail/2323
In November 2024, a company was fined 12,000 yuan because a new employee, who had not completed the mandatory 24-hour safety training, caused an accident due to an operational error. This case served as a stark warning to countless enterprise managers – safety training is not just a "facade project" but a fundamental baseline for business survival. In the same month, the front page of the China Emergency Management News reported on Binzhou City's experience in achieving the digital transformation of safety training through "Four-Chain Integration," highlighting a key trend: enterprise work safety training is shifting from "person-to-person supervision" to "data-driven management."
This article will delve into the necessity of safety training and share insights on how to build an effective safety training management system.
1. Why is Safety Training So Important?
1.1 Preventing Accidents and Injuries
The manufacturing work environment is full of uncertainties. Mechanical failures, chemical leaks, and electrical hazards can all trigger accidents. The purpose of safety training is to equip employees with correct operational procedures and emergency response skills, nipping risks in the bud. For example, common training elements like guidance on using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures are crucial measures to ensure employee safety at work. Through systematic learning, employees can better handle potential dangers, significantly reducing the probability of accidents.
1.2 Complying with Legal Requirements
China's Work Safety Law mandates that enterprises must provide safety education for employees and maintain complete training records as evidence of compliance. Regulations are even stricter for high-risk industries – personnel performing special operations require specialized training, must obtain operation certificates, and undergo periodic re-evaluation. If an enterprise neglects these requirements, consequences upon inspection can range from fines to suspension of operations for rectification, and may even involve criminal liability.
1.3 Enhancing Self-Rescue Capabilities
Safety training not only teaches employees how to avoid accidents but also how to respond to emergencies. In the event of incidents like fires or chemical leaks, employees' abilities in self-rescue and mutual aid can often determine the extent of casualties. Through training, they can learn to use fire extinguishers, perform CPR, and evacuate quickly amidst chaos. Such skills can be a "lifesaver" in critical moments.
1.4 Reducing Downtime Losses
Some might question whether the significant time and effort invested in safety training are worthwhile. The answer is unequivocally yes. Standardized operations not only reduce accidents but also avoid losses associated with work stoppages. Reducing costs related to equipment repairs and legal compensation naturally boosts the enterprise's economic efficiency. For instance, one manufacturing enterprise, by integrating smart training with equipment access controls, saw违规 incidents drop by 65% within a year and a significant increase in production efficiency.
2. How to Build a Safety Culture and Compliance System?
Recognizing the importance of safety training is just the first step. Making it truly effective requires a scientific approach. Here are key practices, from building the training system to fostering the culture.
2.1 Tiered and Categorized Training System
Employees in different roles face varying risks and responsibilities; training content cannot follow a "one-size-fits-all" approach. Categorizing training based on different positions makes it more targeted and effective:
New Employees: Need to complete 24 hours of pre-job training (72 hours for high-risk industries) and pass three-level safety education (plant level, workshop level, team level) to ensure they are familiar with basic regulations. Special Operations Personnel: Must receive specialized training, obtain operation certificates, and undergo periodic re-evaluation to ensure professional skills are proficient. Management Personnel: Need to learn about work safety regulations, the dual prevention mechanism, etc., to enhance their overall management capabilities.
2.2 Making Knowledge "Stick"
Training cannot be just a formality; the key is to ensure employees truly remember and apply what they learn. As an emergency management expert stated, "When safety becomes muscle memory, accidents have nowhere to hide." Consider the following methods to enhance educational effectiveness:
Animation and VR Immersive Experiences: For example, the 60 industry safety animation videos developed by Binzhou City use Virtual Reality (VR) to simulate accident scenarios, allowing employees to experience dangers firsthand. Local Dialect Explanations: Record training content in local dialects for employees in different regions to reduce comprehension barriers. Impactful Warning Education: Regularly screen videos of accident cases within the industry or compile them into booklets. Stories like the one about a worker disabled due to a laser cutter operation error in a machinery factory can deeply resonate with employees using "real-life examples from their surroundings." Combining Tests and Drills: Conduct online tests immediately after training, with automatic retakes for scores below 80; organize emergency drills for scenarios like fires or leaks every six months to ensure skills are practically applied.
2.3 Using Technology to Enhance Training Efficiency
For instance, using QR codes to display training content allows employees to scan and learn, while administrators monitor progress in real-time from the backend. Alternatively, introducing facial recognition at training venues ensures personal attendance and prevents proxy sign-ins. These tools not only improve efficiency but also make training records more credible.
2.4 Full Participation, Building a Safety Culture
Safety is not the responsibility of a single department but a shared duty of every employee. Enterprises can stimulate employee initiative through activities like safety knowledge contests and risk identification reward points. For example, one company regularly holds "Safety Star" selections, rewarding employees who identify hazards or suggest improvements, gradually fostering a culture of "safety for all."
3. How to Build a Safety Training System at Low Cost
Compared to large, comprehensive management systems, QR codes are universally usable and represent a very low-cost solution. Consequently, many manufacturing enterprises, such as LiteAir, Shanxi Coking Coal, and Huanghe Xinye, have chosen CaoLiao QR Code for safety training management.
Using CaoLiao QR Code, you can quickly and freely implement the following application scenarios:
3.1 Safety Training Check-in
Create a safety training check-in QR code and post it at the training site. Employees can check in by scanning the code, enabling thousands to clock in within seconds. Features like GPS location and anti-fraud prevention effectively deter proxy sign-ins. Data syncs to the backend in real-time, allowing administrators to export training records with one click. This provides an objective record of training attendance, offering evidence for future inspections regarding genuine participation, thereby enhancing credibility and authority.
Free creation of Safety Training Check-in QR Code

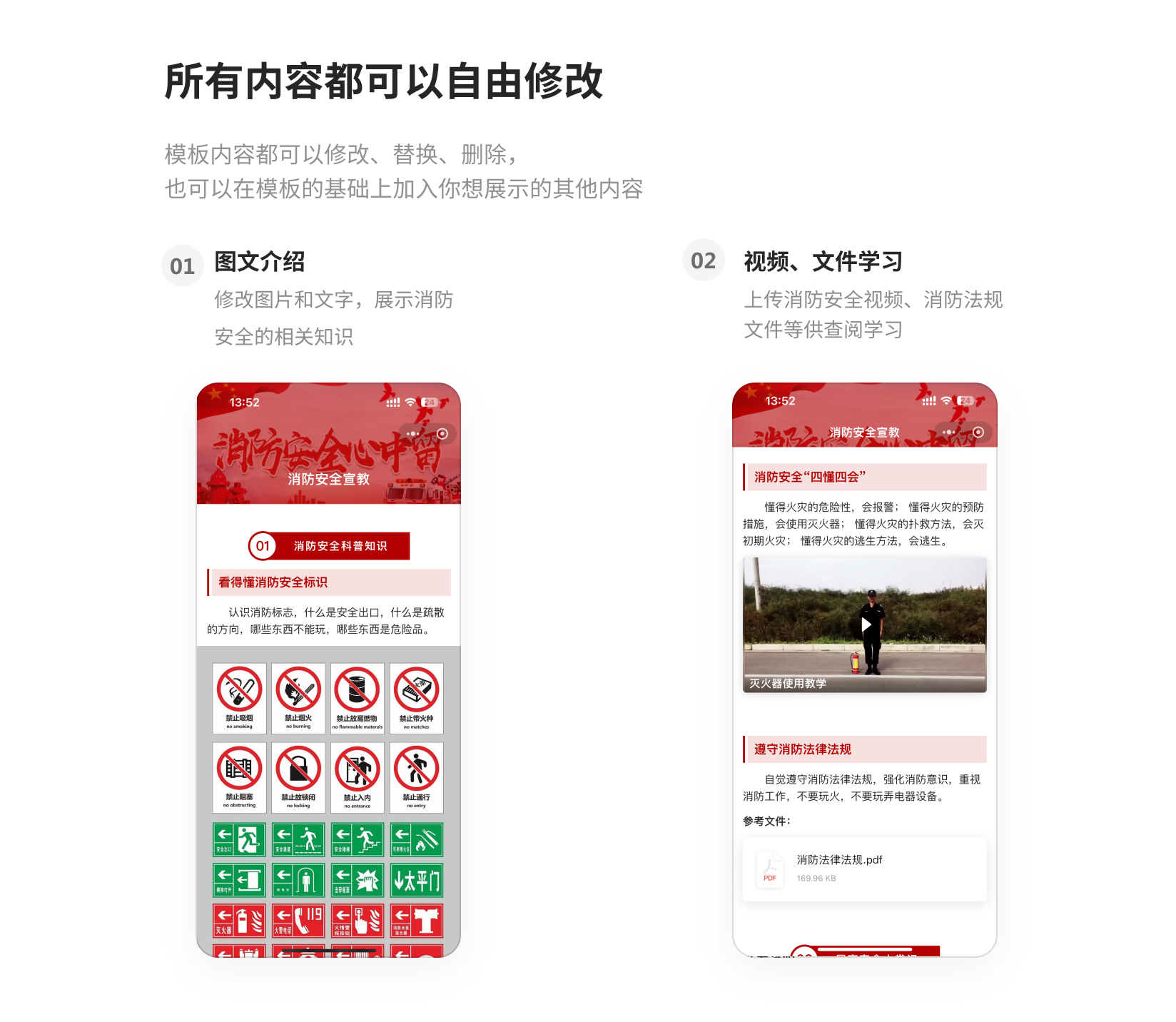
3.2 Work Safety Course Learning
Present work safety course materials, accident warning videos, equipment diagrams, etc., via QR codes. Employees can scan to learn anytime and upload records upon completion. Administrators can clearly see everyone's learning progress in the backend and can even add test questions to the QR code to assess workers' understanding.
Free creation of Work Safety Learning Record QR Code
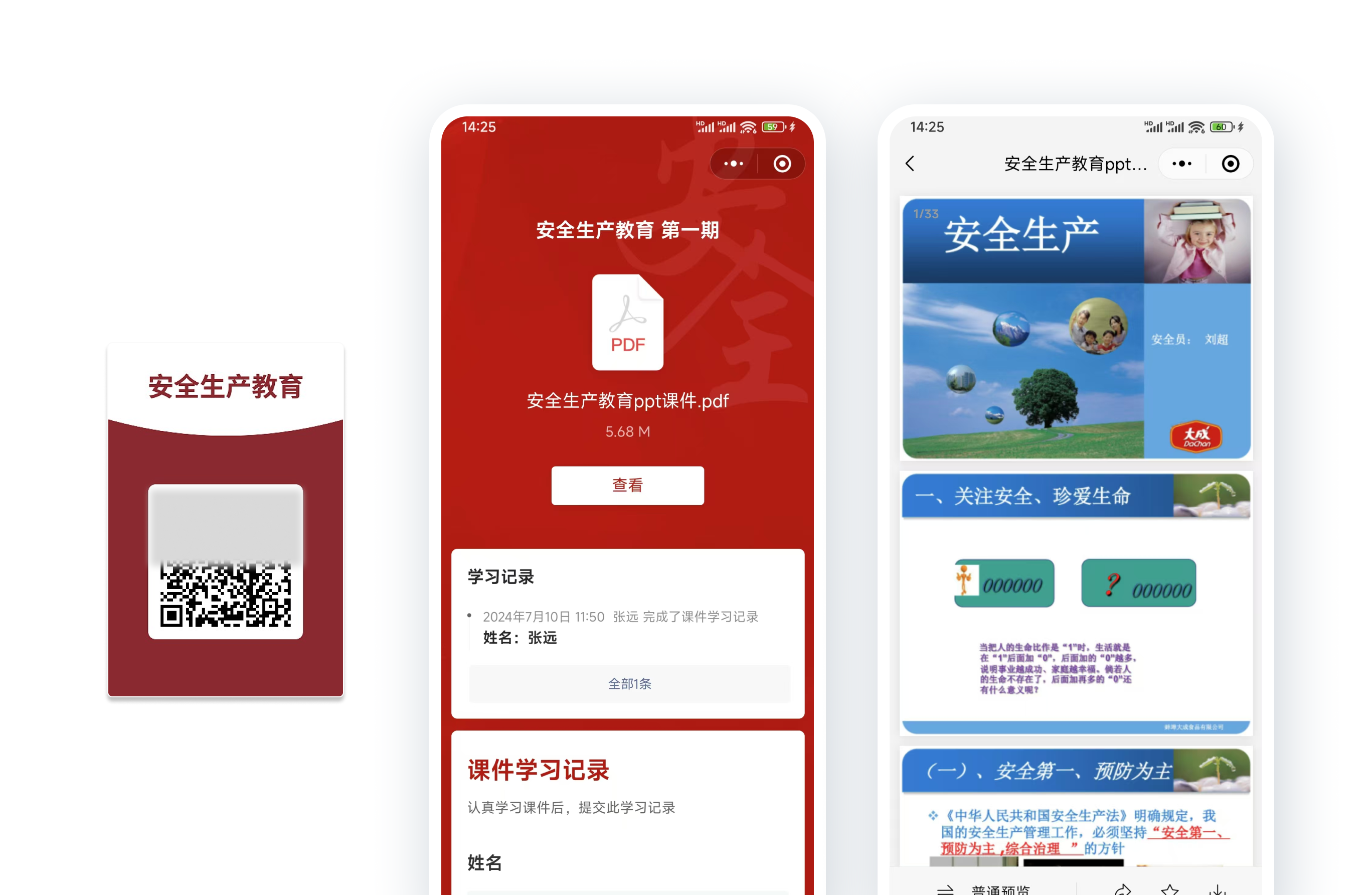
3.3 Work Safety Commitment Letter
Use a QR code to replace the signing of commitment letters. Workers scan the code, read the content, and then provide a handwritten signature to complete the signing record, replacing previous paper-based methods. All signing records are notarized on the blockchain, ensuring credibility.
Free creation of Work Safety Commitment Letter QR Code
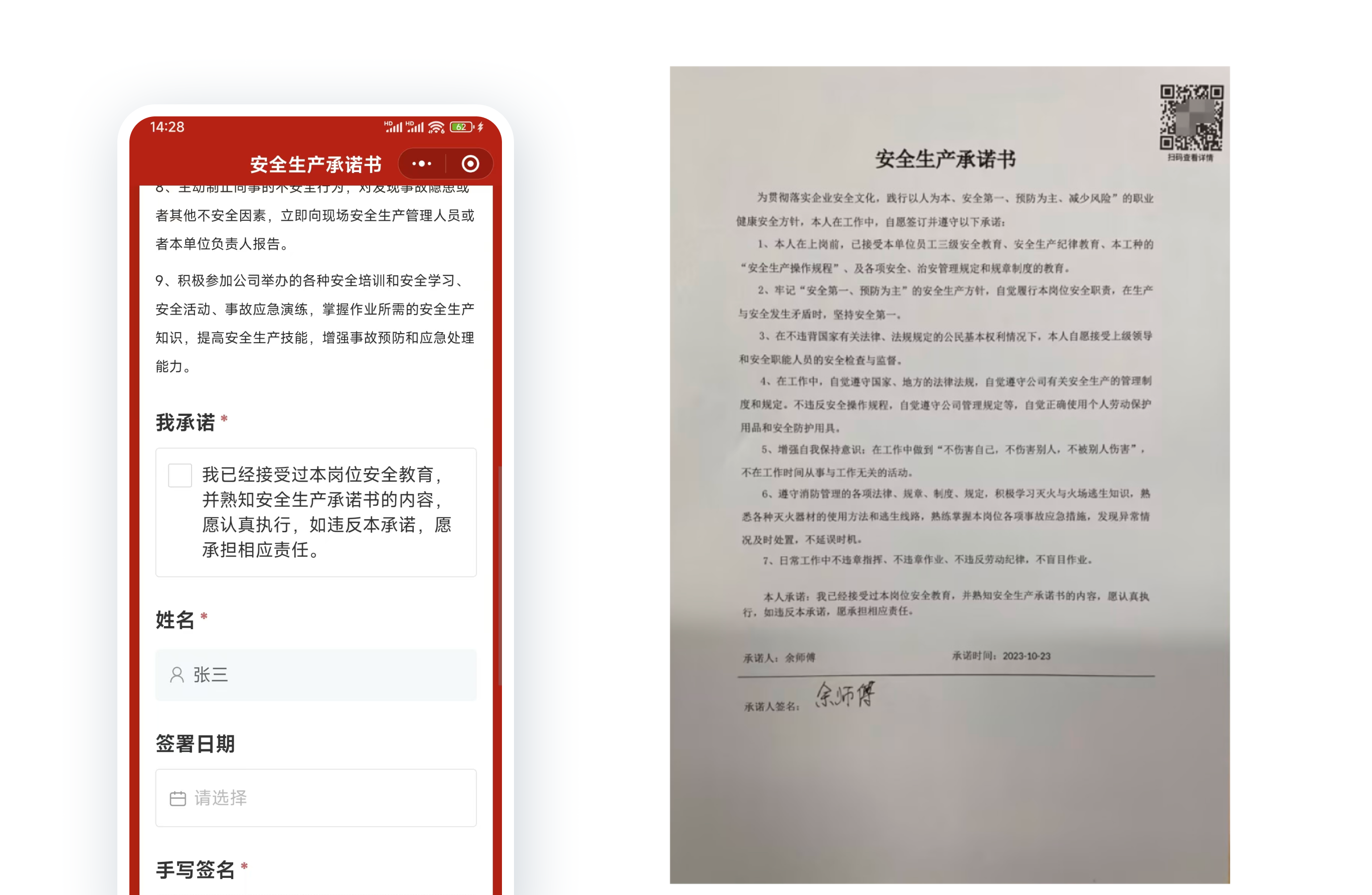
3.4 Safety Education and Promotion
Present safety knowledge, such as fire safety, in various formats like videos, images, and text within a QR code. This replaces paper materials that are difficult to preserve and facilitates richer, more convenient safety knowledge education and promotion.
Free creation of Fire Safety Education QR Code