Optimizing the Application of QR Codes in Operating Room Work – Winner of the Second Prize in the Nursing "Five Small" Innovation Competition
Original: https://cli.im/article/detail/2276

Before we begin, let’s take a look at our finished product. Feel free to scan the QR code and experience it yourself.

We will introduce our QR code from four aspects: background, process, features, and applications.
First, let’s look at the background. "A workman must sharpen his tools if he is to do his work well."
As specialized nurses, our familiarity with specialized instruments directly affects the quality of surgical assistance. Knowing the instruments is just the foundation; the most critical aspect of every surgery is ensuring surgical safety, one part of which is instrument counting. So, how do we perform instrument counting in our work?
"Trusting memory is not as good as writing it down." Long ago, senior colleagues came up with the idea of using written records to assist with counting and verification. However, the drawback of written records is the inconsistency in instrument names. For example, a common tissue forceps might be called "tissue forceps" by one person, "Allis" by another, and "rat-tooth forceps" by someone else. With so many names, confusion is inevitable. Some specialized instruments don’t even have widely recognized names, so they are simply recorded as "additional instruments." This leads to inconsistencies in nursing documentation and a lack of standardization in record-keeping.
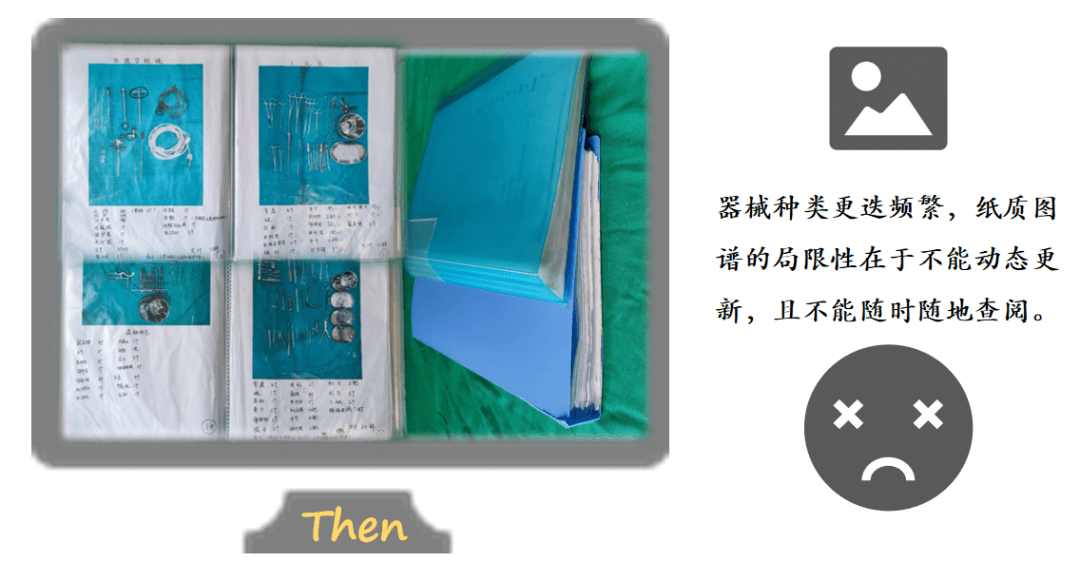
Later, we introduced a thick illustrated manual. Images are more intuitive than text, and the combination of images and text provided a reliable reference. However, the illustrated manual also had its drawbacks. With the introduction of new technologies and surgical procedures across departments, instrument types change frequently. A printed manual cannot be updated dynamically. Moreover, carrying such a heavy manual around is impractical for on-the-spot reference. So, is there a more convenient, faster, and more efficient solution?
Yes, indeed. The widespread use of QR codes in daily life and the trend toward digitalization in hospitals inspired this optimization effort—the departmental information QR code was born.

QR codes offer digitized data sources, zero cost, and are easy and quick to operate, with an intuitive and clear interface.
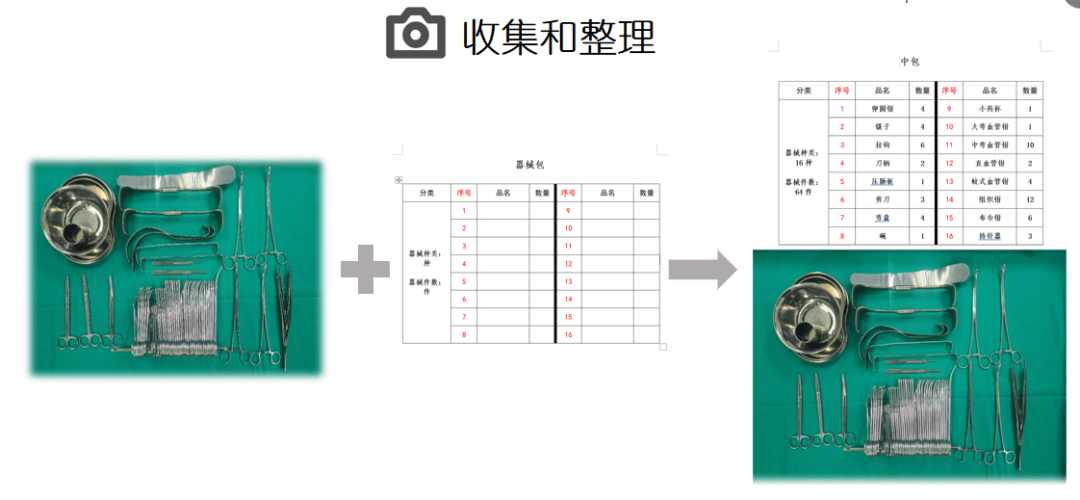
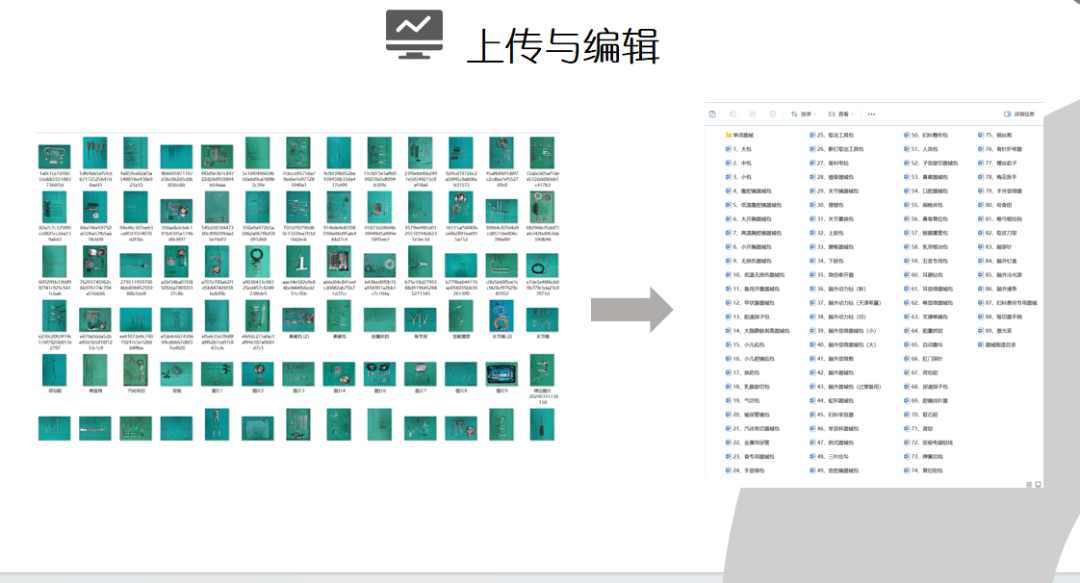
Now, let’s take a closer look at the optimization process. First, we collected and organized the data. We arranged the surgical instruments systematically, took photos for documentation, and compiled the types, names, and quantities of specialized instruments to create a draft of the surgical instrument counting list. After verifying the accuracy, we uploaded the draft to the CaoLiao QR Code platform in directory order, then edited and optimized the pages and content.

The initial QR code opened to an interface in a directory format, as shown in the image. Since the platform lacked a search function, finding the required instruments meant scrolling through the list one by one, which received less-than-optimistic feedback. After repeated trial and error, we further optimized the control panel.
This resulted in a clean, intuitive, and relatively aesthetically pleasing system interface.
After refining these elements, the final version of the QR code was generated—the one you just experienced.
Scanning the QR code leads to an interface with six sections, each representing common surgical specialties. Selecting one takes you to a more detailed subdirectory, allowing users to find the specialized instruments they need.
Now that you have a general understanding of its interface and content, let me summarize its features and advantages.
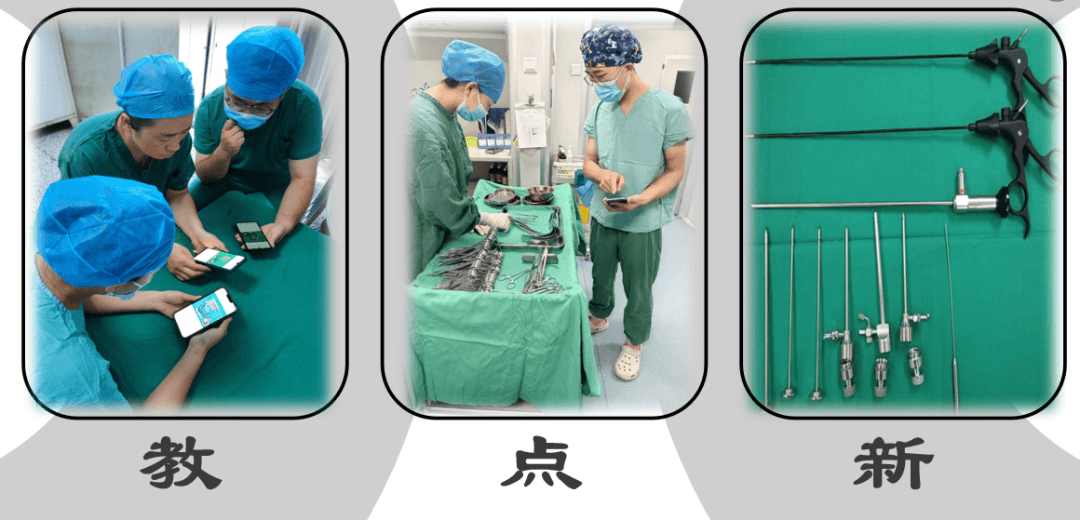
The instrument catalog QR code demonstrates significant advantages in training new nurses in our department. It is primarily used for instrument counting and verification during surgeries. Additionally, the dynamic updates of instrument information adapt to the introduction of new surgical procedures in clinical practice. It also enhances collaboration between our department and the sterile supply department. For example, with some specialized instruments that previously had no standardized names, we could only judge completeness by the total instrument count. If an instrument went missing, we wouldn’t even know which one was lost, making our work highly reactive. With the QR code, instrument names and quantities are clear at a glance, ensuring everyone is well-informed.
In summary, the information QR code generated using the CaoLiao QR Code platform is convenient and quick to use, meeting the need for on-demand access anytime, anywhere. It also supports dynamic updates, facilitating clinical training. As a result, our work efficiency has significantly improved.
Finally, let’s explore its extended applications. After completing the instrument catalog QR code, we didn’t stop there. Through collective effort and momentum, we also developed information QR codes for departmental management systems and complex laparoscopic surgery assistance. These initiatives have transformed our previously shelved and overlooked regulations and guidelines. Now, whether for departmental learning or clinical training, everyone enjoys using QR codes for reference. The combination of images and text has increased engagement and fostered a strong learning atmosphere in our department. We welcome your feedback and suggestions after using it, and we will continue to learn and improve.
Learning knows no bounds. The use of QR codes in our department is both an innovation and a challenge. We will continue to refine other information services based on QR codes, fully implementing the concept of digitizing our departmental workflows.
Original article reprinted from the WeChat public account: Jiyuan Second Hospital [《Second Prize in the Nursing "Five Small" Innovation Competition: Optimizing the Application of Information QR Codes in Operating Room Work》](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_Cey_72-ohn_DlbBCULDgw "《Second Prize in the Nursing "Five Small" Innovation Competition: Optimizing the Application of Information QR Codes in Operating Room Work》")