How to Quickly Build a Fire Safety Management System Using QR Codes
Original: https://cli.im/article/detail/2466
This article is suitable for new users of CaoLiao QR Code. It will guide you through the complete implementation process of a QR code-based fire safety management system from perspectives such as "suitable scenarios for QR codes, setup methods, implementation process, and common operational issues."
1. Which Fire Safety Scenarios Are Suitable for QR Code Management?
The characteristics of the CaoLiao QR Code solution are lightweight, flexible, and low-barrier. It is especially suitable for small and medium-sized units or projects that aim to achieve "traceable inspections, process supervision, and responsibility closure" quickly and at low cost.
Common scenarios include:
- Residential Property Management: Inspections of fire extinguishers, fire hydrants, electrical rooms, fire alarm systems, and daily fire patrols.
- Factories/Warehouses: Daily inspections of fire sandboxes, electrical cabinets, hazardous material areas, fuel storage rooms, as well as management tasks like safety training check-ins and hot work permits.
- Public Buildings: Fire facility inspections and fire drill records in places like schools, hospitals, and shopping malls.
For automatic equipment monitoring or alarm functions, it should be used in conjunction with a Fire Internet of Things (IoT) system. QR codes themselves do not have automatic detection capabilities; they focus more on "process management" and "data archiving."
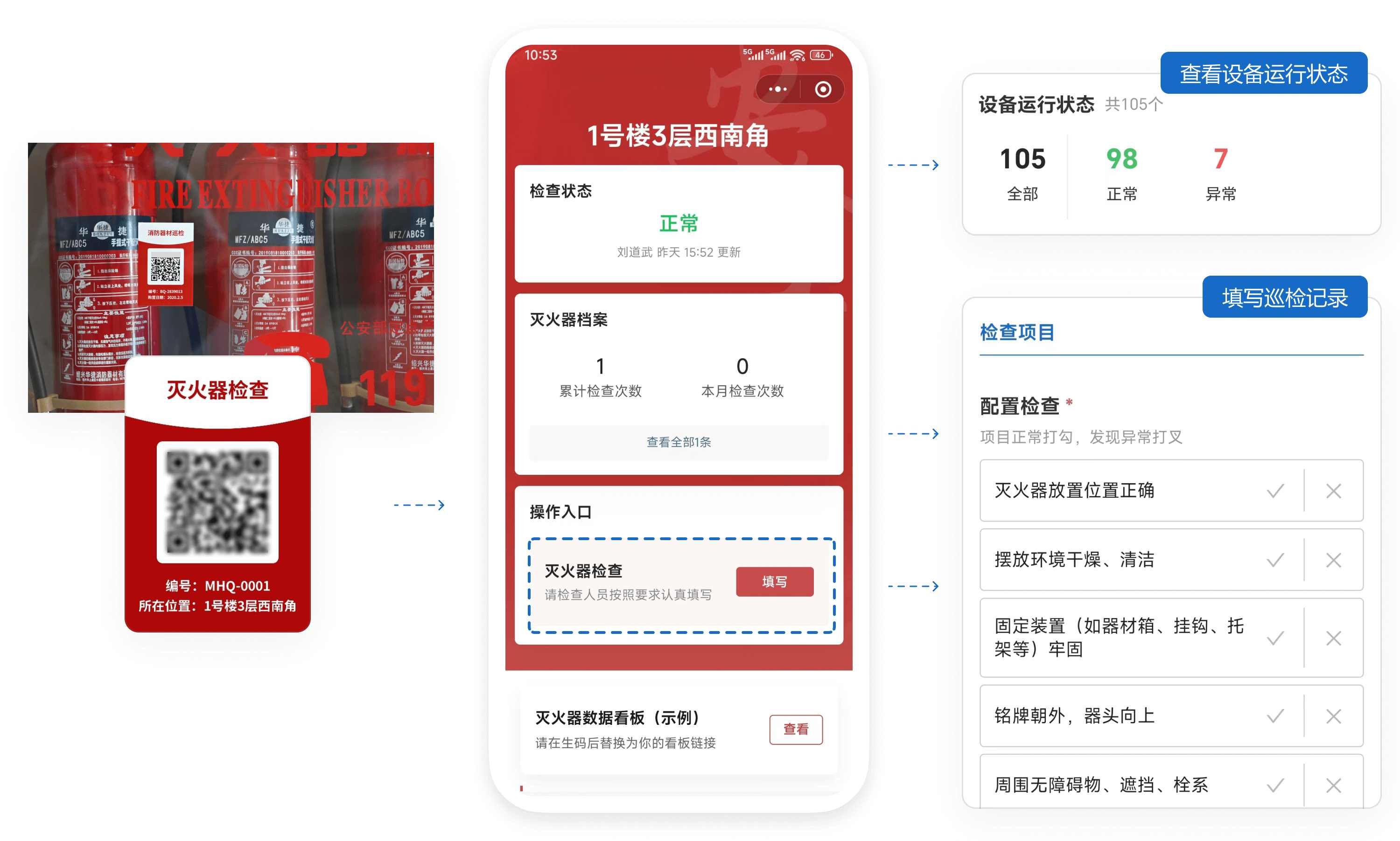
2. System Composition and Concept
CaoLiao QR Code provides a digital management system using QR codes as the entry point. Each fire safety device has its own QR code tag, serving as its electronic record, documenting the entire process from inspection to rectification.
The system consists of five core components:
- QR Code Tags: Affixed to equipment, scanned to view equipment profiles and inspection records; serves as the on-site operation entry point.
- Forms Module: Replaces paper forms, used for filling out inspection items, fault information, and rectification records.
- Status Module: Inspection results automatically update the status (e.g., Normal, Abnormal, Pending Repair).
- Permissions and Notification Mechanism: Different roles have different permissions; abnormal information automatically notifies relevant personnel.
- Data Viewing and Export: Aggregates inspection and maintenance records for all equipment, supports export for archiving.
The system also supports additional features like plans, progress tracking, form review, etc., which can be selected as needed to adapt to different business scenarios. For multi-project sites and large campuses, collaborative management by department, building, or responsibility area is also possible.
3. Basic Setup Process
3.1 Preparation: Asset Inventory and Record Establishment
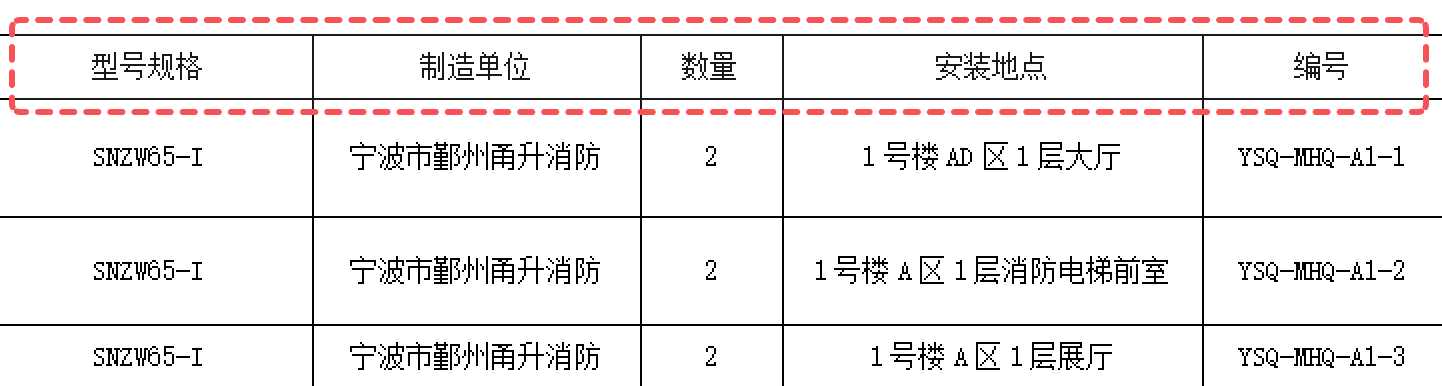
Before setting up the system, conduct a comprehensive inventory of existing fire safety facilities. Using Excel to create a list is recommended for subsequent bulk QR codes generation.
- Asset List: Tally fire safety equipment (fire extinguishers, hydrants, alarms, etc.) within the unit, organizing basic information like ID number, location, model, validity period, responsible person, etc.
- Responsibility Assignment: Clearly define who inspects, who rectifies, and who manages the data. The CaoLiao platform supports permission assignment, but process responsibilities still need to be clarified manually first.
- Form Organization: Gather existing paper forms for later form creation. CaoLiao supports importing images or files to quickly create forms.
3.2 Template Selection and Content Modification
The CaoLiao QR Code platform offers common fire safety scenario templates, including fire extinguisher checks, fire hydrant inspections, fire patrols, etc. These templates reference relevant national standards and industry regulations to ensure compliance; they can be used directly.
You can adjust fields, function settings, label styles, etc., based on the templates to fit your specific management needs.
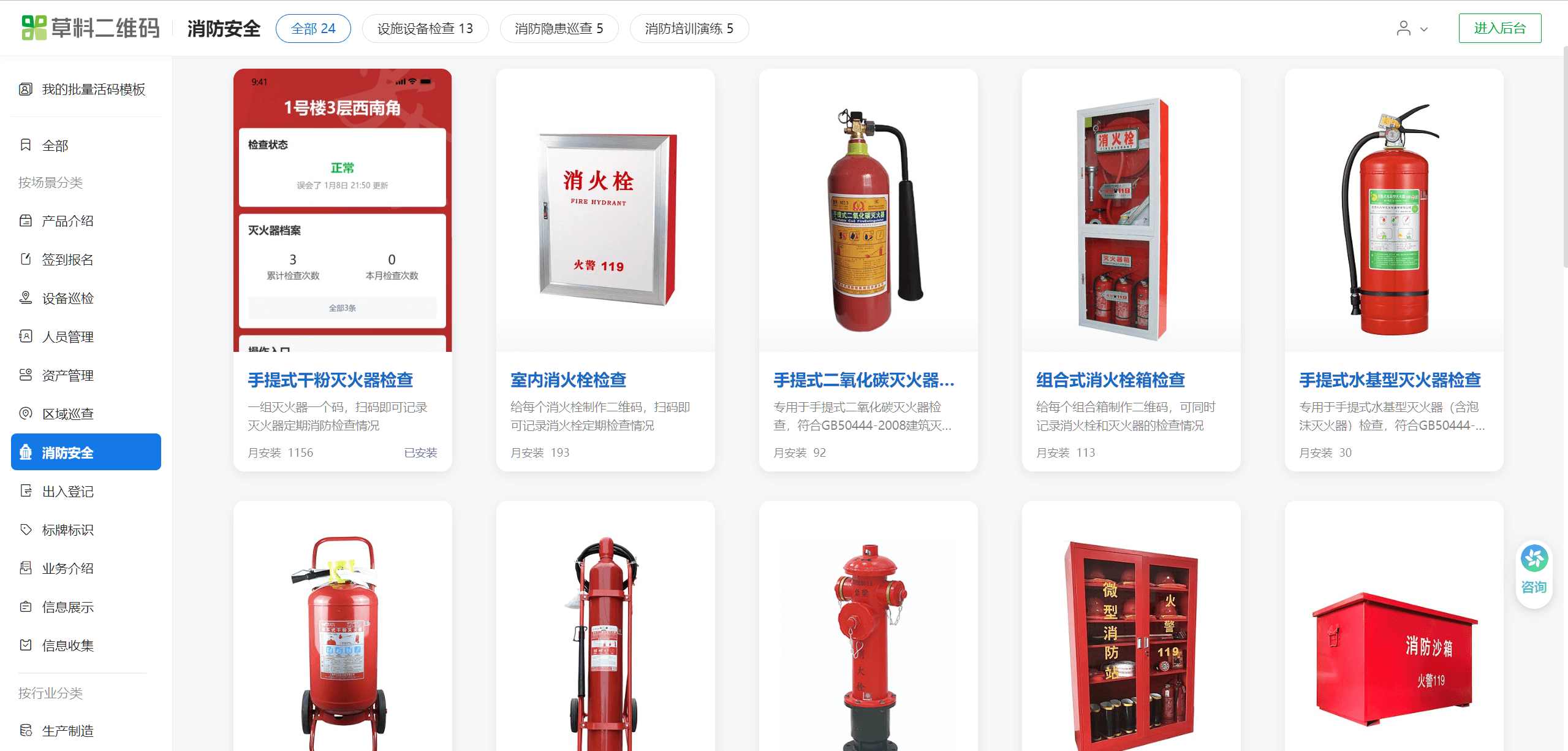
When dealing with a large number of fire safety devices, using the bulk setup method is recommended. For first-time users, start by creating 1-2 QR codes individually to experience the workflow before moving to bulk QR codes generation.
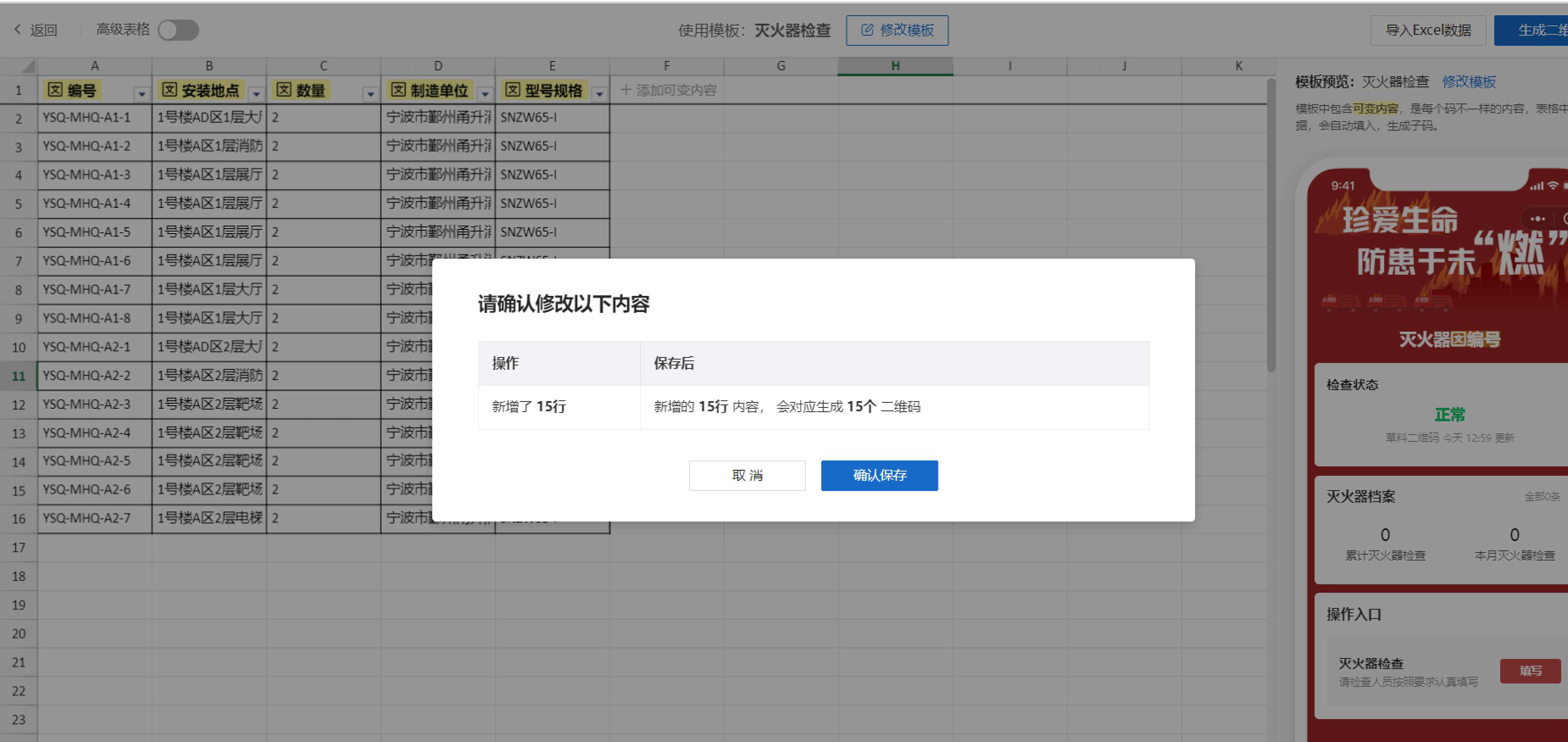
3.3 Bulk QR Codes Generation
After modifying and saving the template, use the "bulk QR codes generation" function to import the prepared equipment list and generate all QR codes at once.
3.4 Print and Affix QR Codes
After generating the QR codes, you can bulk download labels for printing. CaoLiao provides files in various formats like A4 layout PDF, individual PNG images, and vector files, suitable for various printing devices.
- Pilot Phase: Use A4 paper or adhesive labels for quick printing.
- Formal Use: Recommended to choose weather-resistant materials like PVC, stainless steel, or acrylic, especially for outdoor equipment.
Labels should be posted uniformly and standardly in clear, visible locations convenient for inspectors to scan on-site.

4. System Cost Estimation
Many organizations worry that "going digital must be expensive." CaoLiao QR Code's approach is: most basic features are free to use. After initial deployment, you can upgrade to a paid version based on needs:
- Free Version: Supports basic functions like QR code generation, scan-to-view, form filling, data export, etc. No limit on the number of devices or inspection records filled; backend data is stored long-term. Any unit can start with the free version for pilot projects or small-scale application.
- Paid Version: For advanced features like role-based permissions, AI-assisted form filling, multi-level approvals, etc., the annual fee is typically under 3000 RMB, covering the daily management needs of most small and medium-sized enterprises.
Compared to large systems costing hundreds of thousands, this solution is low-cost and quick to deploy.
5. Key Points for Daily Use and Management
Once QR codes are posted, the system is ready for use. It's recommended to gather frontline staff for a brief on-site demonstration of "Scan - Check - Photo - Submit," which can be learned in minutes.
- Frontline Inspectors: Use a mobile phone with WeChat to scan the code, follow prompts to check items, take on-site photos, and submit. No need to install apps or receive specialized training.
- Management Personnel: Can view the status of all equipment at any time, count the number of abnormal devices, missed inspections, and identify unclosed rectification loops. The backend supports one-click Excel export, useful for internal assessment and ready submission during official inspections, reducing the risk of last-minute data preparation.
It's crucial to emphasize that fire safety management is an ongoing task. Launching the system is just the start; subsequent daily maintenance is equally important:
- Label Maintenance: Periodically check QR codes for wear or detachment, and replace them promptly if necessary.
- Form Optimization: After some use, adjust inspection items based on actual conditions, remove unnecessary fields, and improve the filling experience.
- Data Analysis: Use data to identify recurring issues or departments lagging in rectification, providing basis for monthly meetings, training plans, and maintenance priorities.
- Multi-Scenario Expansion: After successfully implementing the fire safety scenario, consider expanding to fire safety training and drill check-ins, safety education, fire safety exams, etc., using the same logic.
6. Common Questions
6.1 Employees Filling Inspection Records Without Being On-Site
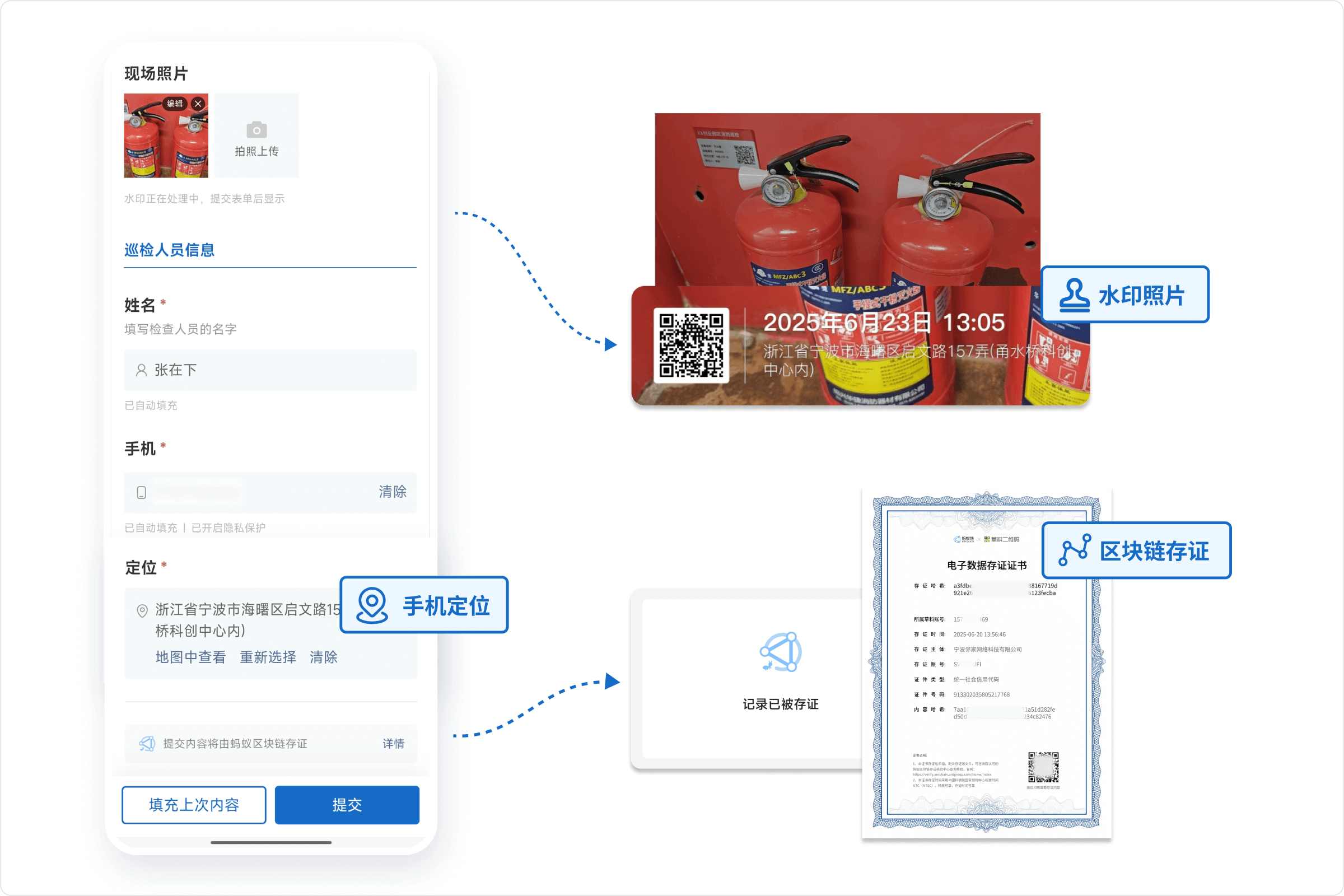
The key to fire inspections is authenticity. The QR code system can ensure data credibility through the following measures:
- Location Restriction: Prevents QR codes from being scanned or opened outside a set radius, ensuring operations occur on-site.
- Mandatory Photo Upload: The image component can be set as required, disabling gallery selection, forcing on-site photo capture. Photos automatically include a watermark (containing recorder, upload time, location, QR code info, etc.).
- Add Handwritten Signature: Increases credibility and adds seriousness to information recording.
- Enable "Blockchain Notarization" Service: Once enabled, each form record is automatically notarized using Ant Group's blockchain technology. Combined with the handwritten signature component, it can replace pen-and-paper signatures, ensuring data is authentic, reliable, tamper-proof, fully traceable, and usable as court-admissible electronic evidence.
All data is saved in the management backend, allowing administrators to conduct random checks to verify inspection authenticity. Using these measures in combination significantly reduces perfunctory inspections.
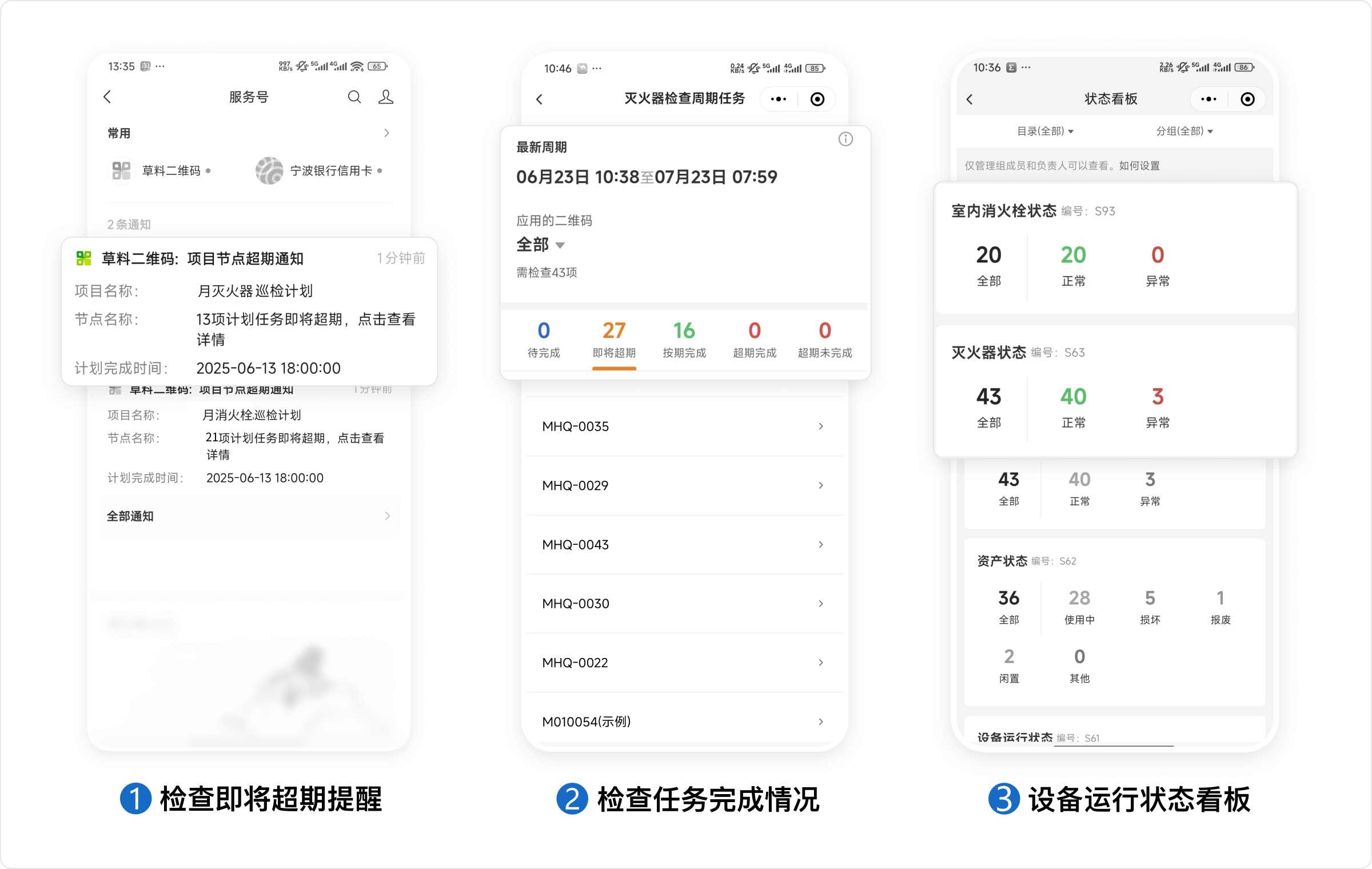
6.2 Too Many Inspection Points, Easy to Miss Checks. What to Do?
You can set up inspection plans in the backend. The system will automatically remind managers when inspection tasks are nearing their deadlines.
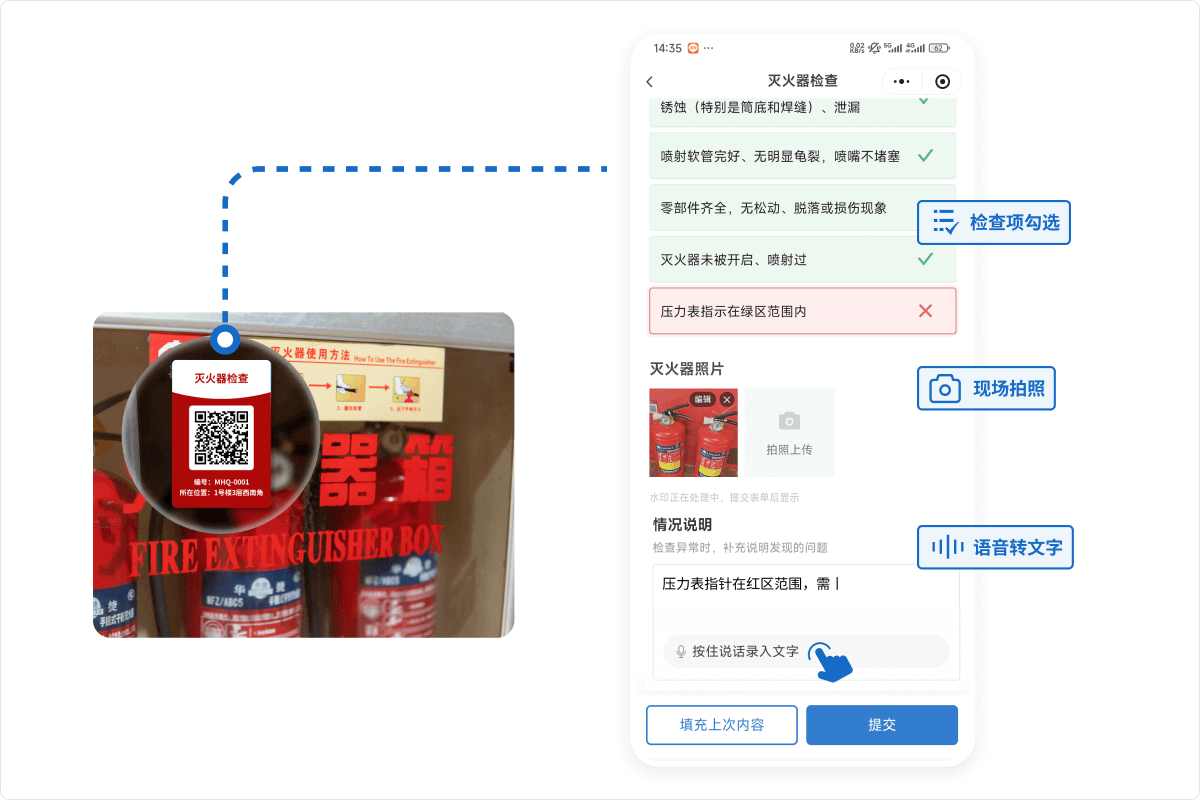
6.3 Employees Find It Troublesome and Reluctant to Fill?
It's recommended to start by simplifying forms: prioritize checkboxes over text fields, use photos where possible, auto-fill repetitive content, and minimize typing. When text descriptions are needed, use voice-to-text to eliminate typing hassle.
You can also enable features like AI-assisted form filling, where the AI automatically recognizes content from on-site photos and populates relevant information into the form, improving efficiency.
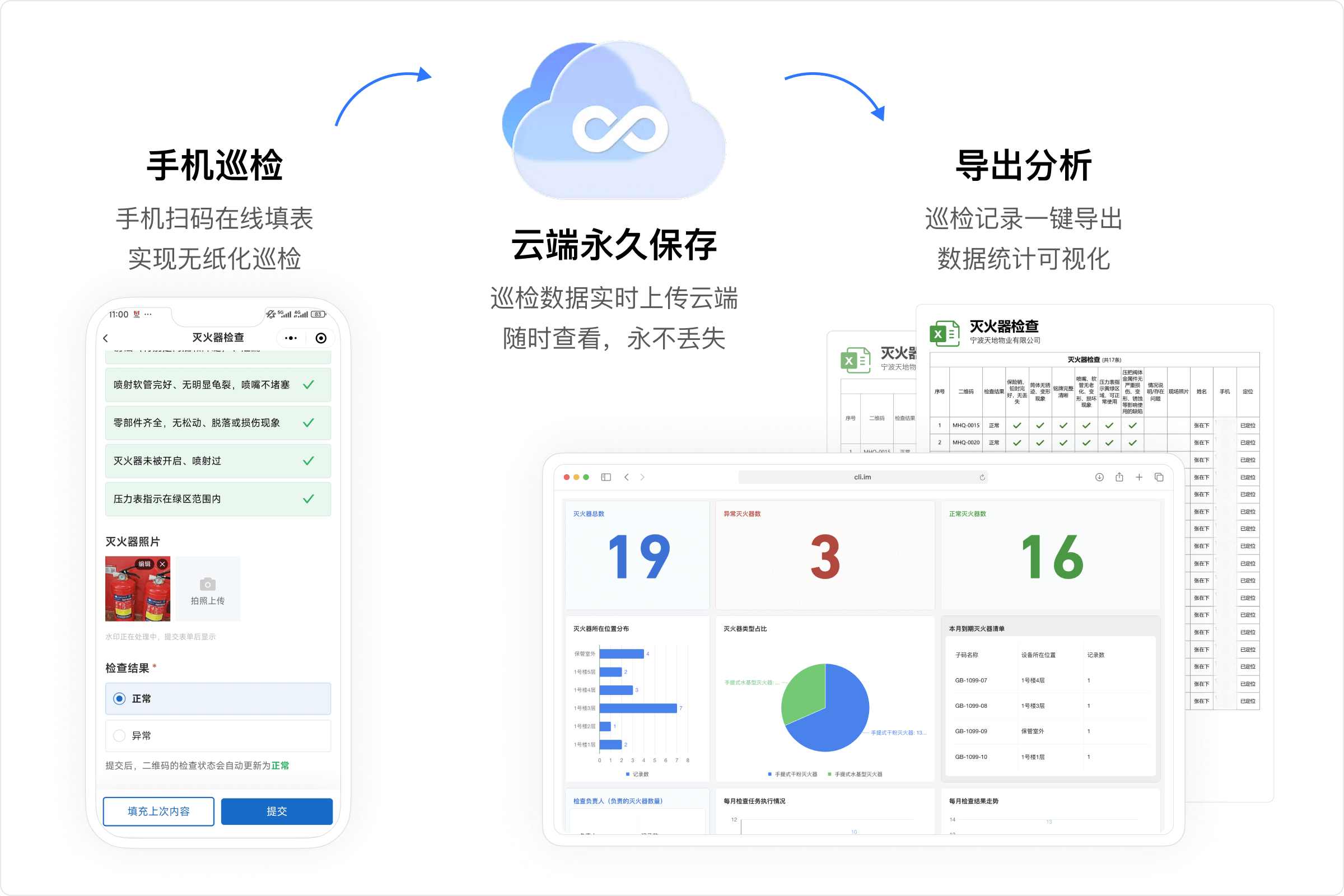
6.4 Are Inspection Records Saved Permanently?
Inspection data is stored permanently. You can view inspection status in the workbench at any time and export data by month, device, area, etc.
7. Summary
The QR code system is not complicated. It simply transforms processes that "should be done but are hard to trace" into a management mechanism with "records, reminders, and closure."
- For SMEs: It doesn't rely on IT support, requires no training, and can be operational in as little as one week.
- For Managers: It's a means to translate policies into actionable execution.
- For Teams: It provides a clear chain of responsibility and efficient collaboration methods.
You can start with a pilot project in one building, one department, or one workshop. Once the process is proven, you can expand it to the fire safety management of the entire organization.